A Values-Aligned Portfolio That Seeks Outperformance and Lower Risk
The Portfolio Managers of the Hennessy Stance ESG ETF(STNC) discuss the portfolio construction process, how the Fund's ESG characteristics compare to the overall market, and the ETF's composition as of the end of 2022.
-
 Kyle BalkissoonPortfolio Manager
Kyle BalkissoonPortfolio Manager -
 Bill DavisPortfolio Manager
Bill DavisPortfolio Manager
Information about the Hennessy Stance ESG ETF (the “Fund”), a semi-transparent actively managed exchange-traded fund ("ETF") with a Portfolio Reference Basket structure:
The Fund is different from traditional ETFs. Traditional ETFs tell the public what assets they hold each day. The Fund will not. This may create additional risks for your investment. For example:
- You may have to pay more money to trade the Fund’s shares. The Fund will provide less information to traders, who tend to charge more for trades when they have less information.
- The price you pay to buy Fund shares on an exchange may not match the value of the fund’s portfolio. The same is true when you sell shares. These price differences may be greater for the Fund compared to other ETFs because it provides less information to traders.
- These additional risks may be even greater in bad or uncertain market conditions.
- The Fund will publish on its website each day a “Portfolio Reference Basket” designed to help trading in shares of the Fund. While the Portfolio Reference Basket includes all the names of the Fund’s holdings, it is not the Fund’s actual portfolio.
The differences between the Fund and other ETFs may also have advantages. By keeping certain information about the Fund portfolio secret, the Fund may face less risk that other traders can predict or copy its investment strategy. This may improve the Fund’s performance. If other traders are able to copy or predict the Fund’s investment strategy, however, this may hurt the Fund’s performance.
For additional information regarding the unique attributes and risks of the Fund, see the Prospectus and SAI.
Key Benefits:
- Values Alignment: We select companies we believe have values aligned with our investors.
- Outperformance: We seek to outperform the overall market.
- Lower Risk: Risk Management is a distinct component of the portfolio construction process.
Would you please describe the Hennessy Stance ESG ETF?
The Hennessy Stance ESG ETF is an actively managed portfolio of approximately 35 to 65 U.S. companies. The Fund was created for investors who want to align their capital with their values while still having the potential opportunity to outperform the overall S&P 500 Index with less risk.
What is the ETF’s portfolio construction process?
We start with companies in the S&P 500 Index and remove approximately 30 stocks that have exposure to weapons, tobacco, and fossil fuels.
Then we overlay our proprietary ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) analysis, which entails ranking, scoring, and weighting the remaining companies against their industry group peers. We consider up to 24 ESG factors in our analysis such as waste profile, water and energy utilization, carbon emissions, labor statistics, compensation, and diversity of board and senior management. The ESG data on the companies is crowdsourced from about 20 different third-party sources that are often issue specific. Based on the results, the bottom 50% of companies are discarded and we continue to analyze the top 50% or approximately 200 stocks.
At the same time, we are performing another analysis based on 20 years of historical financial and market data. This process attempts to predict the top 100 companies that may outperform on a risk-adjusted and total return standpoint. This fundamental model does not look at particular segments of the market; it is only considering the statistically likelihood of outperformance.
The intersection of these two analyses produces our list of ETF holdings that undergo portfolio optimization to minimize tail risk and maximize diversification. We repeat this comprehensive process on a quarterly basis, adding or deleting companies or reweighting stocks based on their relative rank.
Importantly, we are looking for a dispassionate and structured way to invest in ESG companies that is consistently applied over time.
What is an example of a typical ESG holding that might receive a lower ranking in the portfolio?
Ecolab, a global leader in water, hygiene, and energy technologies and services, is a popular ESG-oriented company that passed our stringent ESG and fundamental screens.
However, our optimization analysis determined that Ecolab may potentially add too much risk to the portfolio and, therefore, the stock was assigned a negligible weighting.
What was the portfolio’s composition in the fourth quarter of 2022?
Following the quarterly rebalance, the ETF held 38 companies as of 12/31/22. In terms of sector weightings, the ETF’s holdings included stocks in 9 out of the 11 sectors. There were no holdings in Energy nor Real Estate. Our largest weighting, and largest overweight compared to the S&P 500, was in Health Care. The largest underweight versus the S&P 500 was in Financials.
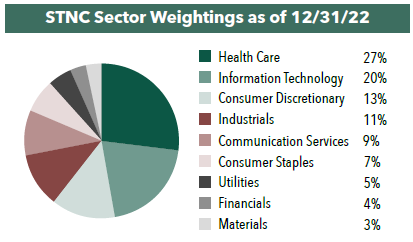
We set maximum weightings when it comes to individual holdings and sectors. The largest an individual holding can be is 3.55% of the portfolio at initial purchase. The largest a sector weighting can be is double the sector weighting in the S&P 500.
- In this article:
- Hennessy Sustainable ETF
